题目
Description
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.
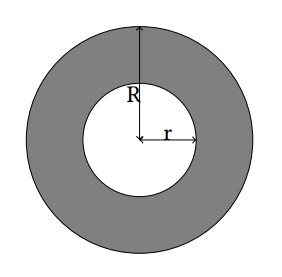
A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 10 5), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers x i, y i (0 ≤ x i, y i ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Output
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
Sample Input
2
2 3
0 0
0 0
2 3
0 0
5 0Sample Output
Case #1: 15.707963
Case #2: 2.250778
题解
纯数学公式推导题
由于牵扯的小数,需要使用 double 进行运算
由于会涉及浮点误差
因此在比较大小的时候需要注意把较大数加上一个偏移量
貌似用海伦公式会出现问题,最好用余弦定理
总共有三种情况
- 完全相离,面积为
0 - 中心重合,面积就是大圆减小圆
- 其他情况,需要4部分相加减计算得出
代码
/* By:OhYee Github:OhYee Blog:http://www.oyohyee.com/ Email:oyohyee@oyohyee.com かしこいかわいい? エリーチカ! 要写出来Хорошо的代码哦~ */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <bitset> using namespace std; const int maxn = 45; const int maxm = 1000005; const double pi = 3.141592653589; int a[maxn]; int dp[maxn][maxm]; struct O { double x; double y; double r; O(double x,double y,double r) { this->x = x; this->y = y; this->r = r; } }; inline double Ha(double a,double b,double c) { double p = (a + b + c) / 2; double ans = sqrt(p*(p - a)*(p - b)*(p - c)); return ans; } inline double distance(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { double ans = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2)); return ans; } inline double Sshanxing(double r,double h) { double th = asin(h / r); return th * r *r / 2; } inline double Ssanjiao(double h,double r) { return sqrt(r*r - h*h)*h / 2; } inline double Syuan(double r) { return pi*r*r; } inline double S(O o1,O o2) { double dis = distance(o1.x,o1.y,o2.x,o2.y); if(dis + 1e-8 > o2.r + o1.r) return 0; if(dis < fabs(o2.r - o1.r) + 1e-8) { double r = min(o1.r,o2.r); return pi * r * r; } double costh1 = (o1.r*o1.r + dis*dis - o2.r*o2.r) / (2 * o1.r*dis); double costh2 = (o2.r*o2.r + dis*dis - o1.r*o1.r) / (2 * o2.r*dis); double th1 = acos(costh1); double th2 = acos(costh2); return th1*o1.r*o1.r + th2*o2.r*o2.r - o1.r*dis*sin(th1); /*double h = Ha(o1.r,o2.r,dis) / dis * 2; double S1 = Sshanxing(o1.r,h) - Ssanjiao(h,o1.r); double S2 = Sshanxing(o2.r,h) - Ssanjiao(h,o2.r); double s = (S1 + S2) * 2; return s;*/ } void Do() { double r,R; double x1,x2,y1,y2; scanf("%lf%lf",&r,&R); scanf("%lf%lf",&x1,&y1); scanf("%lf%lf",&x2,&y2); O o1x(x1,y1,r); O o1d(x1,y1,R); O o2x(x2,y2,r); O o2d(x2,y2,R); double ans = S(o1d,o2d) - S(o1x,o2d) - S(o1d,o2x) + S(o1x,o2x); printf("%.6f\n",ans); } int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); for(int i = 1;i <= T;i++) { printf("Case #%d: ",i); Do(); } return 0; }



 中文博客导航
中文博客导航
 萌ICP备20213456号
萌ICP备20213456号

